
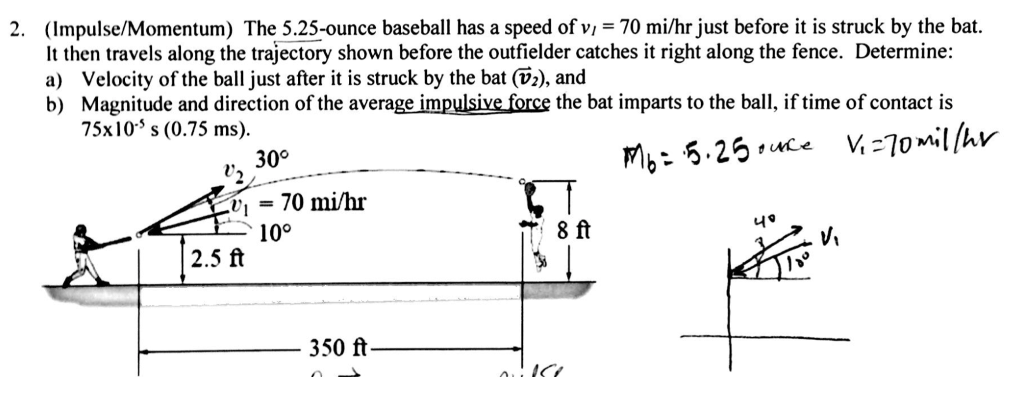
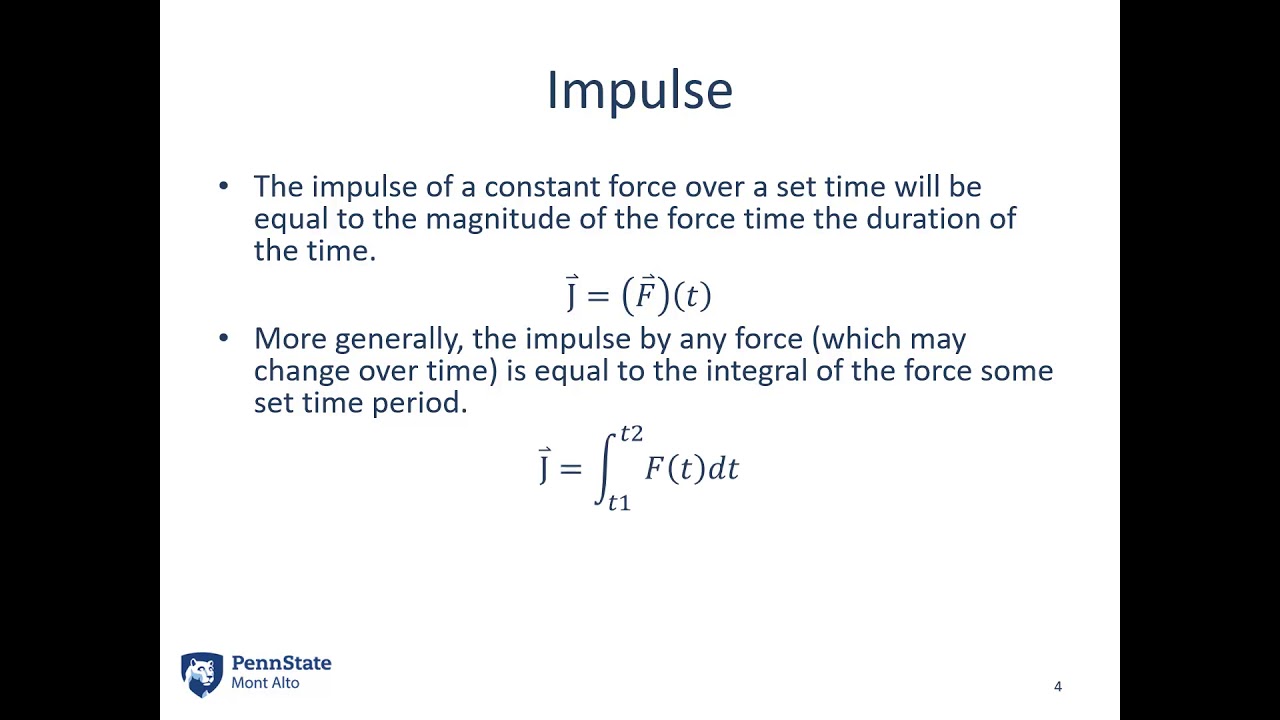
The momentum of a particle is defined as the product of the mass multiplied by the velocity of the motion. THE B6-6 Force (N) 0 Impulse & Momentum Worksheets pg 11. Force (N) 0 Impulse & Momentum Worksheets pg 10. The first number is the thrust of the motor in newtons, the second is the. Two objects, A & B, have identical velocities. Model rocket engines are marked by the a letter, a number, hyphen, and another number. The balls stick together after the impact. Impulsive Force Model Worksheet 2: Impulsive Forces and Momentum. A ball of mass 3.0 kg, moving at 2.0 m/s eastward, strikes head-on a ball of mass 1.0 kg that is moving at 2.0 m/s westward. Here we have guessed that the particles will change direction on collision - they may not! To find the velocities after collision we consider each particle one at a time, choose a positive direction and apply the Impulse-Momentum Principle.įor particle $P$ we will take the direction $\left( \leftarrow \right)$ as the positive. Impulse - Given a force versus time graph or function for a system, calcu- late the change of the systems linear momentum. A force acting on a body will change its momentum. Modeling Instruction - AMTA 2013 1 U9 Momentum - review v3.1 Name Date Pd Impulsive Force Model: Impulse-Momentum Review Sheet 1. The symbol for momentum is (p) so this can also be written as: pmv Momentum is measured in kg ms-1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
